Developmental changes
o Review Kennedy readings for age related changes
Physiological
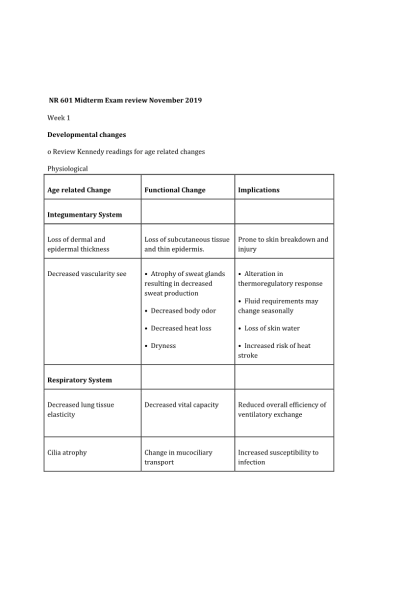
Age related Change | Functional Change | Implications |
Integumentary System |
|
|
Loss of dermal and epidermal thickness | Loss of subcutaneous tissue and thin epidermis. | Prone to skin breakdown and injury |
Decreased vascularity see | • Atrophy of sweat glands resulting in decreased sweat production • Decreased body odor • Decreased heat loss • Dryness | • Alteration in thermoregulatory response • Fluid requirements may change seasonally • Loss of skin water • Increased risk of heat stroke |
Respiratory System |
|
|
Decreased lung tissue elasticity | Decreased vital capacity | Reduced overall efficiency of ventilatory exchange |
Cilia atrophy | Change in mucociliary transport | Increased susceptibility to infection |
Decreased respiratory muscle strength | • Reduced ability to handle secretions and reduced effectiveness against noxious foreign particles • Partial inflation of lungs at rest | Increased risk of atelectasis |
Cardiovascular System |
|
|
Heart valves thicken and become fibrotic | Reduced stroke volume, cardiac output; may be altered | Decreased responsiveness to stress |
Fibroelastic thickening of the sinoatrial node; decreased number of pacemaker cells | Slower heart rate | Increased prevalence of arrhythmias |
Decreased baroreceptor sensitivity (stretch receptors) | Decreased sensitivity to changes in blood pressure | Prone to loss of balance, which increases the risk for falls |
GI |
|
|
Liver becomes smaller | Decreased storage capacity |
|
Decreased muscle tone | Altered motility | Increases risk of constipation, functional bowel syndrome, esophageal spasm, diverticular disease |
Decreased basal metabolic rate (rate at which fuel is converted into energy) |
| May need fewer calories |
NE CONDE)
Lab results
Lab Test | Normal | Changes with age | Comments |
UA |
|
|
|
Protein | 0-5mg/100ml | Rises slightly | May be due to kidney changes with age, urinary tract infection, renal pathology |
Specific Gravity | 1.005-1.020 | Lower max in elderly 1.016-1.022 | Decline in nephrons impairs ability to concentrate urine |
Hematology |
|
|
|
ESR | Men: 0-20 Women: 0-30 | Significant increase | Neither sensitive nor specific in aged |
Iron Binding | 50-160mcg/dl 230-410mcg/dl | Slight decrease Decrease |
|
Hemoglobin | Men: 13-18g/100ml Women: 12-16g | Men: 10-17g Women: None noted | Anemia common in the elderly |
Hematocrit | Men: 45-52% Women 37-48% | Slight decreased speculated | Decline in hematopoiesis |
Leukocytes | 4,300–10,800/mm3 | Drop to 3,100–9,000/mm3 | Decrease may be due to drugs or sepsis and should not be attributed immediately to age |
Lymphocytes | 00–2,400 T cells/mm3 50–200 B cells/mm3 | T-cell and B-cell levels fall | Infection risk higher; immunization encouraged |
Platelet | 150,000–350,000/ | No change in number |
|
Blood Chemistry |
|
|
|
Albumin | 3.5–5.0 | Decline | Related to decrease in liver size and enzymes; protein-energy malnutrition common |
Globulin | 2.3–3.5 | Slight increase |
|
Total serum protein | 6.0–8.4 g | No change | Decreases may indicate malnutrition, infection, liver disease |
Blood urea nitrogen | Men: 10–25 Women: 8–20 mg | Increases significantly up to 69 mg | Increases significantly up to 69 mg |
Creatinine | 0.6–1.5 mg | Increases to 1.9 mg | Related to lean body mass decrease |
Creatinine clearance | 104–124 mL/min | Decreases 10%/decade after age 40 years | Used for prescribing medications for drugs excreted by kidney |
Glucose tolerance | 62–110 mg/dL after fasting; >120 mg/dL after 2 hours postprandial | Slight increase of 10 mg/dL/decade after 30 years of age | Diabetes increasingly prevalent; drugs may cause glucose intolerance |
Alkaline phosphatase | 13–39 IU/L | Increase by 8–10 IU/L | Elevations >20% usually due to disease; elevations may be found with bone abnormalities, drugs (e.g., narcotics), and eating a fatty meal |
o Atypical disease presentations
- Acute abdomen
Absence of symptoms or vague symptoms, acute confusion, mild discomfort and constipation, some tachypnea and possibly vague respiratory symptoms, appendicitis pain may begin in right lower quadrant and become diffuse
- Depression
Anorexia, vague abdominal complaints, new onset of constipation, insomnia..................continue
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Summer 2020 |
| Institution | Chamberlain |
| Contributor | Chantara |