Developmental changes
o Review Kennedy readings for age related changes
Physiological
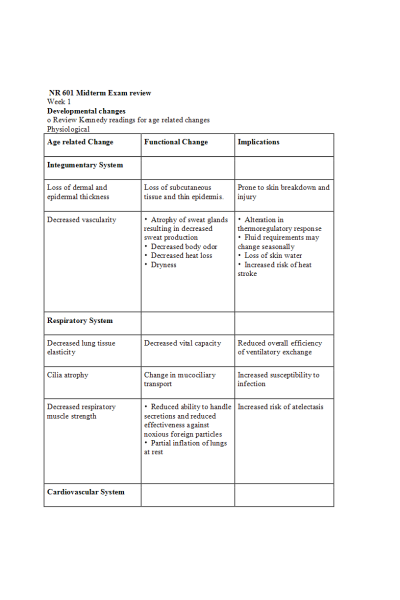
Age related Change | Functional Change | Implications |
Integumentary System |
|
|
Loss of dermal and epidermal thickness | Loss of subcutaneous tissue and thin epidermis. | Prone to skin breakdown and injury |
Decreased vascularity | • Atrophy of sweat glands resulting in decreased sweat production • Decreased body odor • Decreased heat loss • Dryness | • Alteration in thermoregulatory response • Fluid requirements may change seasonally • Loss of skin water • Increased risk of heat stroke |
Respiratory System |
|
|
Decreased lung tissue elasticity | Decreased vital capacity | Reduced overall efficiency of ventilatory exchange |
Cilia atrophy | Change in mucociliary transport | Increased susceptibility to infection |
Decreased respiratory muscle strength | • Reduced ability to handle secretions and reduced effectiveness against noxious foreign particles • Partial inflation of lungs at rest | Increased risk of atelectasis |
Cardiovascular System |
|
|
Heart valves thicken and become fibrotic | Reduced stroke volume, cardiac output; may be altered | Decreased responsiveness to stress |
Fibroelastic thickening of the sinoatrial node; decreased number of pacemaker cells | Slower heart rate | Increased prevalence of arrhythmias |
Decreased baroreceptor sensitivity (stretch receptors) | Decreased sensitivity to changes in blood pressure | Prone to loss of balance, which increases the risk for falls |
GI |
|
|
Liver becomes smaller | Decreased storage capacity |
|
Decreased muscle tone | Altered motility | Increases risk of constipation, functional bowel syndrome, esophageal spasm, diverticular disease |
Decreased basal metabolic rate (rate at which fuel is converted into energy) |
| May need fewer calories |
o Lab results (JACKELINE CONDE).................continue
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Summer 2020 |
| Institution | Chamberlain |
| Contributor | Chantara |