NR 567 Week 8 Final Exam Study Guide
-
$25.00
| Institution | NR 567 Advanced Pharmacology for the Adult-Gerontology Acute Care Nurse |
| Contributor | Jaime Bradely |
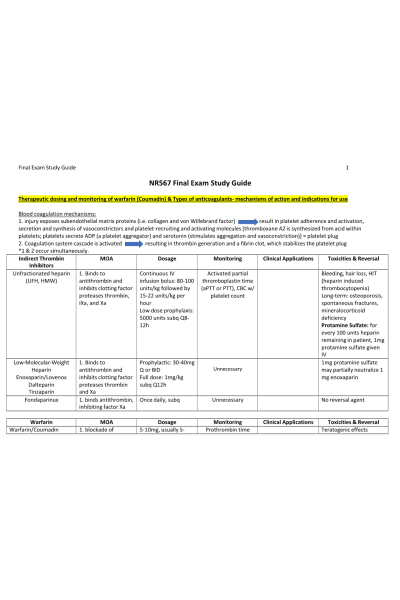
Therapeutic dosing and monitoring of warfarin (Coumadin) & Types of anticoagulants- mechanisms of action and indications for use
Blood coagulation mechanisms:
- injury exposes subendothelial matrix proteins (i.e. collagen and von Willebrand factor) result in platelet adherence and activation, secretion and synthesis of vasoconstrictors and platelet-recruiting and activating molecules [thromboxane A2 is synthesized from acid within platelets; platelets secrete ADP (a platelet aggregator) and serotonin (stimulates aggregation and vasoconstriction)] = platelet plug
- Coagulation system cascade is activated resulting in thrombin generation and a fibrin clot, which stabilizes the platelet plug
*1 & 2 occur simultaneously.
Indirect Thrombin Inhibitors | MOA | Dosage | Monitoring | Clinical Applications | Toxicities & Reversal |
Unfractionated heparin (UFH, HMW) | 1. Binds to antithrombin and inhibits clotting factor proteases thrombin, IXa, and Xa | Continuous IV infusion bolus: 80-100 units/kg followed by 15-22 units/kg per hour Low dose prophylaxis: 5000 units subq Q8- 12h | Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT or PTT), CBC w/ platelet count |
| Bleeding, hair loss, HIT (heparin induced thrombocytopenia) Long-term: osteoporosis, spontaneous fractures, mineralocorticoid deficiency Protamine Sulfate: for every 100 units heparin remaining in patient, 1mg protamine sulfate given IV |
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Enoxaparin/Lovenox Dalteparin Tinzaparin | 1. Binds to antithrombin and inhibits clotting factor proteases thrombin and Xa | Prophylactic: 30-40mg Q or BID Full dose: 1mg/kg subq Q12h |
Unnecessary |
| 1mg protamine sulfate may partially neutralize 1 mg enoxaparin |
Fondaparinux | 1. binds antithrombin, inhibiting factor Xa | Once daily, subq | Unnecessary |
| No reversal agent |
Warfarin | MOA | Dosage | Monitoring | Clinical Applications | Toxicities & Reversal |
Warfarin/Coumadin | 1. blockade of | 5-10mg, usually 5- | Prothrombin time |
| Teratogenic effects |
| gamma-carboxylation resulting in incomplete coagulation of factor molecules that are inactive | 7mg/d Education: increased vitamin K intake (leafy greens) reduce anticoagulant effect of warfarin | (PT) and INR INR gaal:2-3 INR goal w/ artificial heart valves: 2.5-3.5 |
| PO/IV Vitamin K1, FFP, prothrombin complex concentrates (KCentra) |
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Year 2022 |
| Institution | NR 567 Advanced Pharmacology for the Adult-Gerontology Acute Care Nurse |
| Contributor | Jaime Bradely |