xNR 546 Antidepressant and Mood Stabilizer Medication Table
-
$20.00
| Institution | NR 546 Advanced Pharmacology: Psychopharmacology for Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner |
| Contributor |
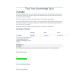
Antidepressant Medications
Name | Indication, starting dose, target symptoms, and affected neurotransmitters | Half-life (T1/2) CYP450 enzyme | Notes/Notable side effects/Precautions |
SSRIs | |||
Citalopram (Celexa) | serotonin reuptake inhibitor (S-RI)
Commonly Prescribed for Depression Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) Panic disorder Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) Social anxiety disorder (social phobia) | Parent drug has 23–45 hour half- life Weak inhibitor of CYP450 2D6 Metabolized by CYP450 3A4 and 2C19 | Notable Side Effects Sexual dysfunction (dose-dependent; men: delayed ejaculation, erectile, dysfunction; men and women: decreased sexual desire, anorgasmia) Gastrointestinal (decreased appetite, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, dry mouth) Mostly CNS (dose-dependent insomnia but also sedation, agitation, tremors, headache, dizziness) Activation (short-term; patients with diagnosed or undiagnosed bipolar or psychotic disorders may be more vulnerable to CNS-activating actions of SSRIs) Sweating (dose-dependent) Bruising and rare bleeding Rare hyponatremia (mostly in elderly patients and generally reversible on discontinuation of citalopram) SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion) |
| The goal of treatment is complete remission of current symptoms as well as prevention of future relapses
How to Dose Initial 20 mg/day; increase by 20 mg/day after 1 or more weeks; maximum 40 mg/day; single-dose administration, morning or evening |
| Other Warnings/Precautions Use with caution in patients with history of seizures Use with caution in patients with bipolar disorder unless treated with concomitant mood-stabilizing agent When treating children, carefully weigh the risks and benefits of pharmacological treatment against the risks and benefits of nontreatment with antidepressants and make sure to document this in the patient’s chart. Whenever possible, warn patients and their caregivers about the possibility of activating side effects, and advise them to report such symptoms immediately. Monitor patients for activation of suicidal ideation, especially children and adolescents |
Escitalopram (Lexapro) | SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Commonly Prescribed for | Mean terminal half-life 27–32 hours Substrate for | Notable Side Effects Sexual dysfunction (men: delayed ejaculation, erectile dysfunction; men and women: decreased sexual desire, anorgasmia) Gastrointestinal (decreased appetite, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, dry mouth) Mostly |
.......... Continue
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Year 2022 |
| Institution | NR 546 Advanced Pharmacology: Psychopharmacology for Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner |
| Contributor | |