NR 507 Week 7 Quiz Study Guide (Musculoskeletal, Gastrointestinal, Endocrine)
-
$29.00
| Institution | Chamberlain |
| Contributor | James |
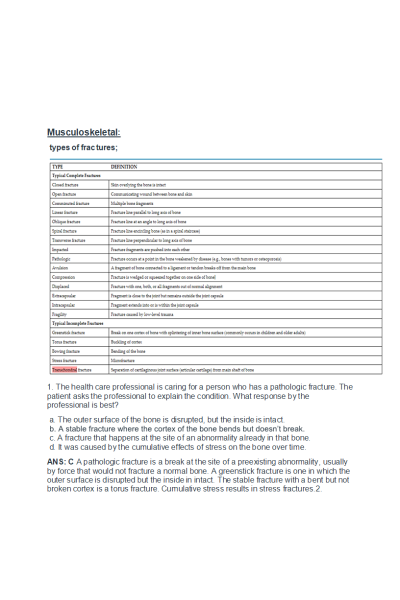
Musculoskeletal:
Types of fractures Definitions;
- Question: The health care professional is caring for a person who has a pathologic fracture. The patient asks the professional to explain the condition. What response by the professional is best?
- Question: A health care professional is providing education to a group of seasonal athletes. What type of fracture does the professional warn them to avoid?
- Question: Improper reduction or immobilization of a fractured femur can result in which outcome after cast removal?
- Question: What is the tear in a ligament referred to as?
- Question: Which type of osteoporosis would a person develop after having the left leg in a cast for 8 weeks to treat fracture of the tibia and fibula?
- Question: A patient is brought to the Emergency Department after being found by neighbors. The patient says she has been lying on the floor in the house for 3 days. What action by the health care professional is best?
- Question: The health care professional teaches a group of seniors that the most common clinical manifestation of osteoporosis is which of these?
Osteoporosis (types of fracture that is prevalent; screening test for osteoporosis);
Hip fractures, vertebral fractures (most common osteoporotic fracture)
- Question: A health care professional is providing education to a group of seasonal athletes. What type of fracture does the professional warn them to avoid?
- Question: By the time osteoporosis is visible on an x-ray examination, up to what percent of bone has been lost?
- Question: A patient has a bone density T score of -2.8. What diagnosis does the health care professional educate the patient on?
- Question: Which type of osteoporosis would a person develop after having the left leg in a cast for 8 weeks to treat fracture of the tibia and fibula?
- Question: In osteoporosis, the receptor activator of nuclear factor κB (RANK) activates what?
- Question: The health care professional teaches a group of seniors that the most common clinical manifestation of osteoporosis is which of these?
Transchondral fractures; Separation of cartilaginous joint surface (articular cartilage) from main shaft of bone
Gout (cause of pain);
- Question: A person in the health care clinic has gout. In order to prevent a common complication, what self-care measure does the health care professional teach the person about?
- Question: What causes the crystallization within the synovial fluid of the joint affected by gouty arthritis?
- Question: The pathophysiologic presentation of gout is closely linked to the metabolism of which chemical?
- Question: A patient in the clinic has calcium crystals that are associated with chronic gout. How does the professional document this finding?
Pathological features of degenerative joint disease;
Osteomalacia; epicondylopathy;
Hip fractures secondary to osteoporosis;
Diagnosing rhabdomyolysis
- Rapid breakdown of muscle that causes release of myoglobin into blood stream.
- Question: A student asks for an explanation of rhabdomyolysis. What response by the professor is best?
- Question: A patient is brought to the Emergency Department after being found by neighbors. The patient says she has been lying on the floor in the house for 3 days. What action by the health care professional is best?
- Question: A patient reports joint stiffness with movement and joint pain in weightbearing joints that is usually relieved by rest. What treatment option does the health care professional discuss with the patient?
Gastrointestinal:
Reflux Esophagitis;
- Question: A patient asks the healthcare professional to describe the cause of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). What response by the professional is best?
- Question: A patient has been diagnosed with reflux esophagitis (GERD). What instruction by the healthcare professional is most appropriate?
- Question: A class of students has learned about contributing factors to duodenal ulcers. What statement indicates to the professor that the students need a review?
Characteristics of Gastric Ulcers;
Increased serum gastrin, located in upper abdomen, intermittent pain, pain-antacid-relief pattern
- Question: A peptic ulcer may occur in all of these areas except which?
- Question: A class of students has learned about contributing factors to duodenal ulcers. What statement indicates to the professor that the students need a review?
Causes of elevated liver function tests;
Increase biliary
Bulimia nervosa;
- Question: A person has abnormally severe tooth decay and erosion of the tooth enamel. What problem should the health care professional assess the person for? a. Anorexia nervosa b. Binge eating c. Bulimia d. Refeeding syndrome
Anorexia Nervosa;
- Question: A health care professional is caring for a patient admitted to the hospital with severe anorexia. What action by the health care professional would be most important?
- Question: A patient weighs 82 pounds and is hospitalized for anorexia. In order to prevent refeeding syndrome, how many calories should the person eat in the first two days?
- Question: A family is concerned that their most elderly member is not eating. What information about the anorexia of aging does the health care professional provide the family? (Select all that apply.)
Interpretation of Hepatitis B vaccine serological markers (for example, results show HbsAb-what information would you provide the patient?)
Endocrine:
Pathophysiology of Type 1 diabetes;
Classic signs of diabetes mellitus and their causes;
Kidney function in the patient with diabetes insipidus;
- Question: What is diabetes insipidus a result of?
- Question: A patient who is diagnosed with a closed head injury has a urine output of 6 to 8 L/day. Electrolytes are within normal limits, but the antidiuretic hormone (ADH) level is low. Although the patient has had no intake for 4 hours, no change in the polyuria level has occurred. What treatment or diagnostic testing does the healthcare professional prepare the patient for?
- Question: Which laboratory value is consistent with diabetes insipidus (DI)?
- Question: A patient has nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (DI). What treatment does the healthcare professional anticipate for this patient?
Chronic complications of diabetes mellitus;
- Question: A patient with several risk factors is concerned about developing type 2 diabetes. The healthcare professional advises the patient to lose weight, explaining that obesity is an important risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus because it causes what?
- Question: A student asks the professor to differentiate Type 2 diabetes mellitus from Type 1. The professors’ response would be that Type 2 is best described as what?
- Question: A person diagnosed with type 1 diabetes experienced an episode of hunger, lightheadedness, tachycardia, pallor, headache, and confusion. The healthcare professional teaches the person that what is the most probable cause of these symptoms?
- Question: A chronic complication of diabetes mellitus is likely to result in microvascular complications in which areas? (Select all that apply.)
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Spring 2020 |
| Institution | Chamberlain |
| Contributor | James |