NR 507 Week 4 Midterm Concepts
-
$20.00
| Institution | NR 507 Advanced Pathophysiology |
| Contributor | Mireille |
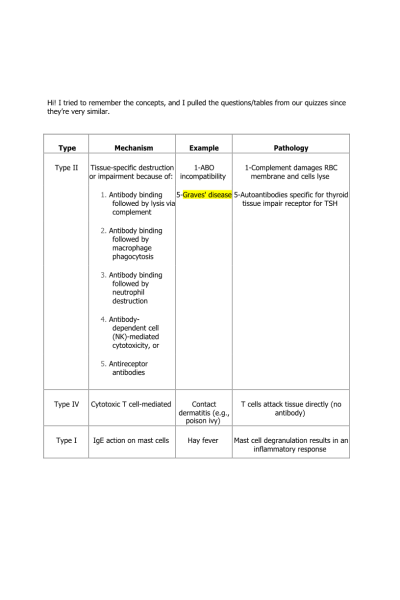
Hi! I tried to remember the concepts, and I pulled the questions/tables from our quizzes since they’re very similar.
Type |
Mechanism |
Example |
Pathology |
Type II |
Tissue-specific destruction or impairment because of: |
1-ABO incompatibility |
1-Complement damages RBC membrane and cells lyse |
| 1. Antibody binding followed by lysis via complement | 5-Graves' disease | 5-Autoantibodies specific for thyroid tissue impair receptor for TSH |
| 2. Antibody binding followed by macrophage phagocytosis |
|
|
| 3. Antibody binding followed by neutrophil destruction |
|
|
| 4. Antibody- dependent cell (NK)-mediated cytotoxicity, or |
|
|
| 5. Antireceptor antibodies |
|
|
Type IV |
Cytotoxic T cell-mediated |
Contact dermatitis (e.g., poison ivy) |
T cells attack tissue directly (no antibody) |
Type I |
IgE action on mast cells |
Hay fever |
Mast cell degranulation results in an inflammatory response |
Type III |
Antigen-Antibody complex deposited in tissues |
Raynaud’s phenomenon |
Complex deposited in small peripheral vessels in cool temperatures leading to vasoconstriction and blocked circulation |
Damage occurs with ABO incompatibility because complement damages RBC membrane causing cell lysis.
An example of a primary immunodeficiency is Chronic Granulomatous Disease.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) = autoimmune. Signs and Symptoms of SLE? Facial rash confined to the cheeks. Tissue inflammation, vasculitis, rash, tissue inflammation........... Continue
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Year 2022 |
| Institution | NR 507 Advanced Pathophysiology |
| Contributor | Mireille |