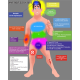
B Vitamins
Water-soluble
Most common types:
- B1 (thiamin) growth and function of various cells
- B2 (riboflavin) is a key component of coenzymes involved with the growth of cells, energy production, and the breakdown of fats, steroids, and medications
- B3 (niacin) works in the body as a coenzyme, helps to convert nutrients into energy, create cholesterol and fats, create and repair DNA, and exert antioxidant effects
- B5 (pantothenic acid) used to make coenzyme A (CoA)
- B6 (pyridoxine) breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats B12 (cobalamin) needed to form red blood cells and DNA
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Spring Session |
| Institution | Chamberlain |
| Contributor | Marla |