BIOS 242 Week 5 Concepts; The Immune System
-
$29.00
| Institution | BIOS 242 Fundamentals of Microbiology with Lab - Chamberlain |
| Contributor | Anika Fultz |
Week 5 Concepts: The Immune System
Epidemiology
Prepare: Epidemiology
- The principal government agency responsible for tracking infectious diseases in the United States is the
- The study of the frequency and distribution of a disease in a defined population is .
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assigns the most virulent microbes known to cause human disease to biosafety level 4.
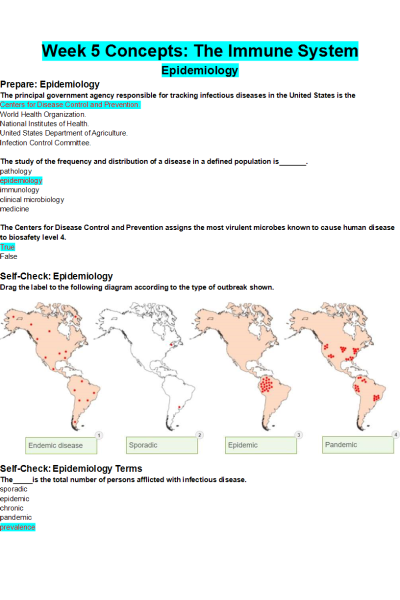
Self-Check: Epidemiology
Drag the label to the following diagram according to the type of outbreak shown.
Self-Check: Epidemiology Terms
- The is the total number of persons afflicted with infectious disease.
- A is an epidemic occurring over multiple continents.
Reflect: Epidemiology
- The prevalence rate of tuberculosis in one particular county in Texas is 7/1000 people, while the incidence rate for 2011 is 2/1000 people. Analyze this data and summarize the situation.
- The number of new cases of a disease in a population over a specific period of time compared with the healthy population is the .
- A disease that has a steady frequency over time in a particular geographic location is referred to as .
- The study of the frequency and distribution of a disease in a defined population is .
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention mandates that some diseases must be reported, while it is not necessary for others. This is so that
- The total number of deaths in a population due to a disease is the rate.
Innate Immune Function
Prepare: Innate Immune Function
- Which of the following DO NOT form part of physical barriers?
- The immune defenses are divided into how many basic categories?
- Chemical barriers include: (Select all that apply)
- Monocytes differentiate into when the cells migrate to tissues.
Self Check: Nonspecific Chemical Defenses
- Nonspecific chemical defenses include:
Self Check: Phagocytosis
- Which of the following is not an event of phagocytosis?
Self Check: Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
Self Check: White blood cells
- Which of the white blood cells produces chemicals that can attack large helminths?
Self Check: Interferon production
- Host cells that produce interferon after viral attack can protect themselves from the invasion.
Self Check: Membrane attack stage
- The membrane attack stage of the complement cascade involves:
Self Check: Inflammation
- Which of the following is mismatched in relation to inflammation?
Reflect: Innate Immune Function
- The chemical found in tears and saliva that hydrolyzes the peptidoglycan in certain bacterial cell walls is:
- The blood cells that function in allergic reactions and inflammation, contain peroxidase and lysozyme, and particularly target parasitic worms and fungi are:
- The least numerous of all white blood cells that release histamine during inflammation and allergic reactions are:
- The branch of the immune system present at birth is called:
- The process in which the phagocytic cells move to the bacteria:
- Match the following cells with their characteristics:
- List the following steps of phagocytosis in order:
Adaptive Immune Function
Prepare: Adaptive Immune Function
- A foreign molecule that causes a specific immune response is a(n):
- Acquired specific immunity involves the response of:
- Plasma cells:
Self Check: Specific immunity
- Specific immunity provides long-lasting protection through the production of:
Self Check: Adaptive immune system
- The cells of the adaptive immune system are educated to distinguish your cells from invading pathogens, cells that would respond to self-antigens are destroyed in immune tolerance. This property of adaptive immunity is attributed to the
Self Check: T cells
- T cells mature in the bone marrow?
Self Check: Properties of effective antigens
Properties of effective antigens include all of the following except:
Self Check: Humoral immunity
- T helper cells play a pivotal role in
Self Check: MHC-II antigen
Self Check: Antigen presenting cells
- Antigen presenting cells:
Self Check: Killer T cells
For a CD8 killer T cell (TC) to become activated, it must recognize a foreign peptide complexed with self MHC-I and mount a direct attack upon the target cell.
Self Check: Lymphocytes
- Which lymphocyte secretes antibodies in a specific immune response?
Self Check: Antibodies
Self Check: Antigen response
- A patient was never exposed nor vaccinated against chickenpox. A couple days ago the patient was exposed, and the patient currently has chicken pox virus. Which antibody would you expect to have the highest titer based on this exposure?
- Two months later, the same patient is then exposed to chicken pox virus again. Which immunoglobulin will be present in the highest amount after this new exposure?
Self Check: Artificial active immunity
- An example of artificial active immunity would be vaccination.
Reflect: Adaptive Immune Function
- The antibody-secreting progeny cells of a B-cell clone are called:
- MHC molecules are found on all cells except:
- Small foreign molecules that are too small by themselves to elicit an immune response are termed:
- The immunoglobulin class that has a dimer form found in mucus, saliva, colostrum, and other body secretions is:
- The immunoglobulin class that is the only one capable of crossing the placenta is:
- Generates many B cells and T cells that are activated against specific antigens:
- Cytotoxic T cells:
- Specific immunity provides long-lasting protection through the production of:
- Match the following to their description:
- Match the following:
- Which of the following would be affected when T helper cells are destroyed in HIV infections? Select all that apply.
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Uploaded 2023 |
| Institution | BIOS 242 Fundamentals of Microbiology with Lab - Chamberlain |
| Contributor | Anika Fultz |