BIOS 242 Week 2 Concepts; Classification and Nutrition
-
$25.00
| Institution | BIOS 242 Fundamentals of Microbiology with Lab - Chamberlain |
| Contributor | Anika Fultz |
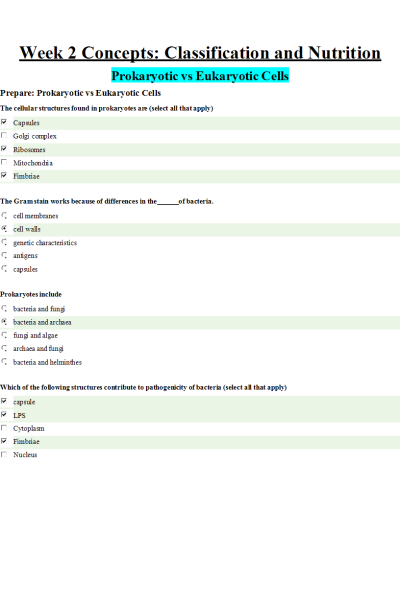
Week 2 Concepts: Classification and Nutrition
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
Prepare: Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
- The cellular structures found in prokaryotes are (select all that apply)
- The Gram stain works because of differences in the of bacteria.
Prokaryotes include
- Which of the following structures contribute to pathogenicity of bacteria (select all that apply)
Self-Check: Bacteria and Archaea
- Drag the cell types to the three respective highlighted images at the bottom.
Self-Check: Bacteria External Cell Structures
- Drag the description to the correct image.
Self-Check: Bacterial Cell Envelope
- Drag the items to the corresponding cell wall.
Self-Check: Bacterial Internal Structure
- Drag and drop the terms to the two respective locations at the bottom of this cell.
Self Check: Bacterial Cell: External
- Drag labels to their correct placement on the chart.
Self Check: Bacterial Cell - Cell envelope
Self Check: Bacterial Cell - Internal
- Drag labels to their correct places on the chart.
Self-Check: Matching Definitions
- Which of the following is mismatched?
Reflect: Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
- Select all that apply. Three general shapes of bacteria are
- Select all that apply. A new microorganism is discovered, and you have identified it as bacteria because it
- Match the terms to their description.
- Match the terms to their description.
- Match the terms to their description.
- Select all that apply. Arrangements found among the general shapes of bacteria
Eukaryotic Cell and Cell Division
Prepare: Eukaryotic Cell and Cell Division
- In producing beer and wine, humans have exploited the microbial ability to ferment sugar to alcohol. The microbes responsible for this process are .
- The vesicle that originates from the Golgi apparatus and contains a variety of digestive enzymes is the .
- When a eukaryotic cell is not undergoing mitosis, the DNA and its associated proteins appear as a visible, thread-like mass called
- Which of the following is not a stage of mitosis?
- Helminth is another word for
Self-Check: Eukaryotic Reproduction
- Drag the appropriate reproduction method to the correct row in the table.
- The different types of reproduction found in various eukaryotic organisms
Self-Check: Mitosis
- Drag and drop label to its respective location.
Self-Check: Stages of Mitosis
- Drag each stage of mitosis below to its corresponding description.
Self-Check: Types of Eukaryotic Microbes - Algae
- Algae does not cause any type of harm to human health.
Self-Check: Fungi
- The first antibiotic, penicillin, was developed by this type of eukaryotic organism.
Self-Check: Helminths
- Some helminths are , having both male and female organs.
Reflect: Eukaryotic Cell and Cell Division
- The , a, group of large free-living eukaryotes use pseudopodia for movement.
- The two major groups of helminths are and .
- In humans, helminths generally infect the .
- Fungi that grow as yeasts at one temperature but as molds at another temperature are called .
- _____ causes thrush in infants.
- Yeast reproduce by which sometimes appear as miniature snowmen.
- ______ spores are formed by mitosis and spores are made by meiosis.
- The long, thread-like branching cells of molds are called .
- Red tide is a/an that produces a neurotoxin that can be dangerous to humans.
- _______ is obtained from undercooked infected meat or exposure to infected cats.
- After returning from a trip to Africa, Tom feels tired and weak and has severe anemia. A blood smear reveals a protozoan in his blood and the health care provider diagnoses malaria caused by .
- In several rounds of mitotic nuclear division occur prior to cytoplasmic division.
Viruses
Prepare: Viruses
- Host cells of viruses include .
- Two noncellular agents, smaller than viruses, are infectious RNA strands called and infectious proteins called .
- Viruses .
Self-Check: General Characteristics of Viruses
- Drag and drop terms to their respective locations on the diagram.
Self-Check: Genetic Material of Viruses and Virus Replication
- Drag the correct terms to complete the sentences below.
Self-Check: Replication in Animal Viruses
- Match the stages of animal viral replication to their description.
Self-Check: Viruses
- Drag the correct term to complete the sentences below.
Reflect: Viruses
- Host cells of viruses include .
- Bovine spongiform encephalopathy disease is
- Two noncellular agents, smaller than viruses, are infectious RNA strands called and infectious proteins called .
- Viruses that infect bacteria are specifically called .
- During lysogeny, an inactive prophage state occurs when the viral DNA is inserted into the host .
- Persistent viruses that can reactivate periodically are .
- The core of every virus particle always contains .
- A/an is the protein shell around the nucleic acid core of a virus.
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Uploaded 2023 |
| Institution | BIOS 242 Fundamentals of Microbiology with Lab - Chamberlain |
| Contributor | Anika Fultz |