ACCT 212 Week 5 Homework
- Question:
- Required:
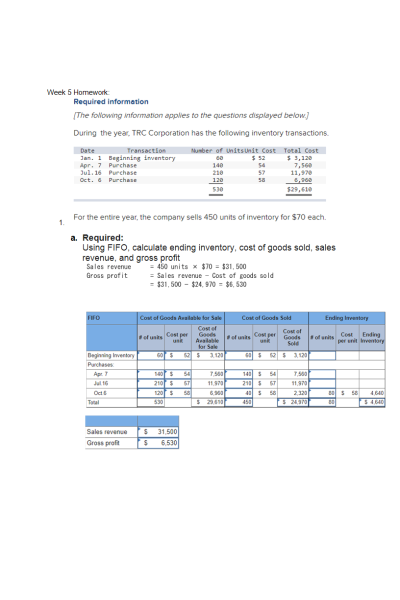
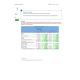
Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit
Sales revenue = 450 units × $70 = $31,500
Gross profit = Sales revenue − Cost of goods sold
= $31,500 − $24,970 = $6,530
- Question:
- Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit.
Sales revenue = 450 units × $70 = $31,500
Gross profit = Sales revenue − Cost of goods sold
= $31,500 − $25,410 = $6090
- Question:
- Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit. (Round "Average Cost per unit" to 2 decimal places and all other answers to the nearest whole number.)
4. Question:
- Determine which method will result in higher profitability when inventory costs are rising.
- Question:
Required:
- Calculate cost of goods sold for each company.
- Question:
- Calculate the inventory turnover ratio for each company.
Cost of goods sold/average inventory (inventory beginning + inventory ending)/2 Average Inventory:
Lewis Cost of Goods Sold $197,200/ ($20,000 + $14,000)/2
$197,200/ $17,000 = 11.6
Clark Cost of Goods Sold $132,600/ ($46,000 + $56,000)/2
$132,600/ $51,000 = 2.6
- Question:
- Calculate the average days in inventory for each company. (Round your intermediate calculations to 1 decimal place.)
8. Question:
- Which company appears to be managing its inventory more efficiently?
9. Question:
Required:
- Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31, using the specific identification method. The October 4 sale consists of purses from beginning inventory, the October 13 sale consists of one purse from beginning inventory and two purses from the October 10 purchase, and the October 28 sale consists of three purses from the October 10 purchase and four purses from the October 20 purchase.
10. Question:
- Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.
Ending inventory: (1 x $750) + (8 x $760)
$750 + $6,080 = $6,830
Cost of goods sold: (6 x $730) + (5 x $740) + (3 x $750)
$4,380 + $3,700 + $2,250 = $10,330
11. Question:
- Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.
Date Number of Units Unit Cost Total Cost Oct 1 Begin In 6 $730 $4,380
Oct 10 Purch | 5 | $740 | $3,700 |
Oct 20 Purch | 4 | $750 | $3,000 |
Oct 30 Purch | 8 | $760 | $6,080 |
12. Question:
- Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31. (Round your intermediate and final answers to 2 decimal places.)
ACCT 212 Week 5 Homework - Practice:
- Question:
- Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit.
- Question:
- Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit.
- Question:
- Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit. (Round "Average Cost per unit" to 2 decimal places and all other answers to the nearest whole number.)
- Question:
Which method will result in higher profitability when inventory costs are declining?
- Question: Sundance Systems has the following transactions during July.
- Required:
Record the transactions of Sundance Systems, assuming the company uses a perpetual inventory system. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.)
Required:
- Calculate cost of goods sold for each company.
- Question:
- Calculate the inventory turnover ratio for each company.
- Question:
- Calculate the average days in inventory for each company.
9. Question:
- Which company appears to be managing its inventory more efficiently?
10. Question:
Required:
h. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31, using the specific identification method. The October 4 sale consists of purses from beginning inventory, the October 13 sale consists of one purse from beginning inventory and two purses from the October 10 purchase, and the October 28 sale consists of three purses from the October 10 purchase and four purses from the October 20 purchase.
11. Question:
- Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.
12. Question:
j. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.
13. Question:
k. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31. (Round your intermediate and final answers to 2 decimal places.)
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Summer 2021 |
| Institution | ACCT 212 Financial Accounting |
| Contributor | Jessica Brown |